Resources
Resources
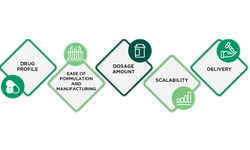
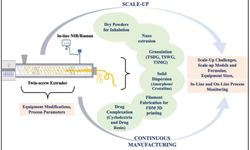
Discover a comprehensive array of resources dedicated to powder compression, including scientific papers, application bulletins, and invaluable support for R&D, scale-up, and production. Gain complete access to our extensive resource library by signing in.
559
results
Date